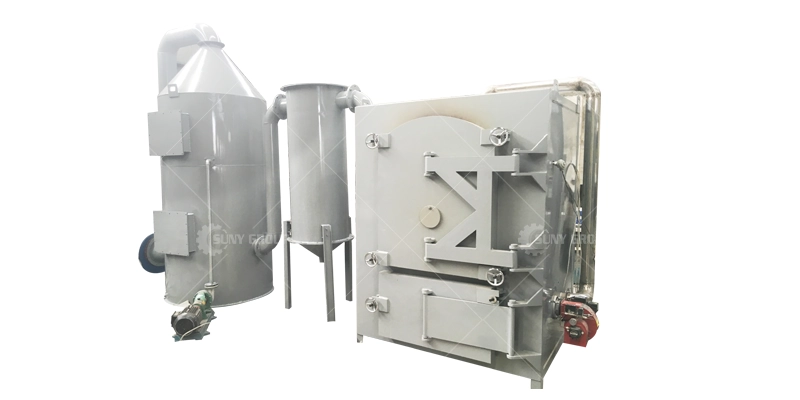
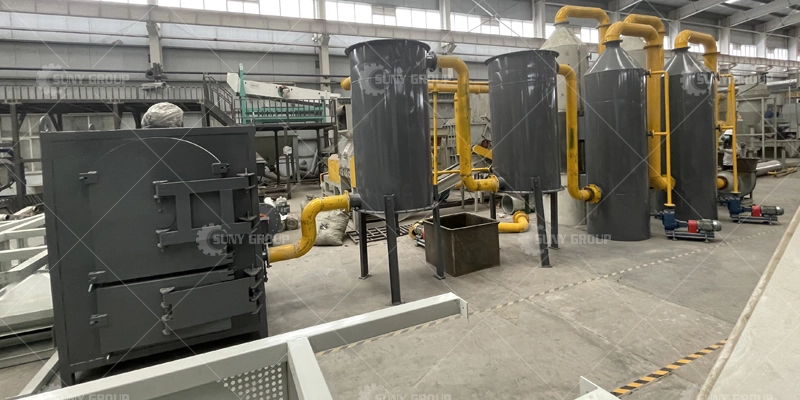
Carbonization furnace
Carbonization Furnace processes plastic-encapsulated components, IC chips, and MLCCs by using high-temperature, low-oxygen pyrolysis to carbonize resins and preserve metals. Equipped with sealed design and gas purification, it ensures safe, clean operation and prepares materials for further metal recovery.
Details
This Carbonization Furnace is a specialized heat treatment unit designed primarily to remove organic resin encapsulation layers (Epoxy resin, Phenolic resin, etc.) from electronic components.
Core Function: Utilizes high-temperature Pyrolysis technology to convert the hard plastic/resin wrapping the metal and ceramic into fragile Carbon (Char) and volatile gases.
Target Materials:
- IC Chips (BGA, QFP, SOP, etc.): To extract internal Gold bonding wires, Copper lead frames, and Silicon wafers.
- MLCC (Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors): To remove external encapsulation and binders, recovering internal Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag), and Nickel (Ni) electrode layers.
- Plastic Packed Components: Various plastic-encapsulated diodes, transistors, power modules, etc.
Ultimate Goal: To separate metals/ceramics from organic matter, providing clean raw materials for subsequent physical crushing, screening, or hydrometallurgy, while avoiding metal oxidation and loss caused by direct incineration.

Working Principle
1.The equipment employs an “Oxygen-free/Low-oxygen Pyrolysis Carbonization” process.Anaerobic Environment: Before heating, the furnace chamber is vacuumed or purged with inert gas (typically Nitrogen, $N_2$) to remove oxygen. This is a critical step to prevent Copper (Cu) and other base metals from oxidizing and turning black at high temperatures, which would affect recovery value
2.High-Temperature Pyrolysis: The furnace temperature is raised to 300°C – 600°C (depending on the resin type). At this temperature, the solid polymer resin chains break, decomposing into oil gas (volatiles) and fixed carbon (solid residue)
3.Resin Carbonization: The originally hard epoxy resin layer turns into loose, porous black carbon (Char) with very low adhesion. It can be completely detached from the metal parts with light mechanical crushing.
4.Off-gas Treatment:
Resins in electronic components often contain Brominated Flame Retardants. Pyrolysis generates toxic harmful gases (Dioxin precursors, HBr, VOCs). Standard configuration includes:
- Condenser: Condenses pyrolysis oil gas into liquid tar for collection (can be used as fuel by-product).
- Scrubber (Spray Tower): Uses alkaline liquid to neutralize acidic gases (like HBr, HCl).
- Activated Carbon/UV Photolysis: Adsorbs residual organic volatiles to ensure compliant emissions.