What types of circuit boards can a PCB sorting and recycling line process?
Every year, over 50 million tons of e-waste are generated globally, and printed circuit boards (PCBs) are among the most valuable—and challenging—components to recycle. Packed with copper, gold, silver, and rare metals, PCBs are the gold mines of electronic waste.
Why PCB Type Matters in Recycling
Different PCBs vary dramatically in:
- Metal content
- Layer structure
- Base materials
- Hazardous substances
A modern PCB sorting and recycling line is designed to identify, classify, and process these differences efficiently, maximizing recovery while minimizing environmental impact.
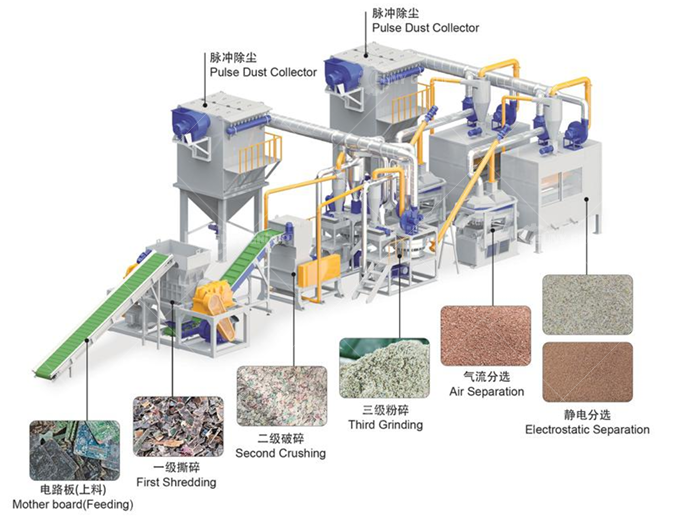
1. Single-Sided Circuit Boards (Low-Grade PCBs)
Common sources:
- Household appliances
- Toys
- Power supplies
- Simple control panels
- Key characteristics:
- Components mounted on one side
- Lower copper and precious metal content
- Often phenolic or paper-based substrates
Recycling insight:
These boards are typically processed in high-throughput, automated lines. While metal value per ton is lower, volume makes them profitable when efficiently sorted.
Best for recyclers focusing on scale and consistency.
2. Double-Sided Circuit Boards (Mid-Grade PCBs)
Common sources:
- Consumer electronics
- Industrial controllers
- Inverters and power modules
- Key characteristics:
- Components on both sides
- Higher copper density
- Mixed solder types
Recycling insight:
A PCB sorting line separates these boards based on thickness, copper ratio, and component density, preparing them for optimized crushing and separation.
Stat fact: Double-sided PCBs can contain up to 20–30% copper by weight, making them a strong revenue contributor.
3. Multilayer Circuit Boards (High-Grade PCBs)
Common sources:
- Servers
- Telecom equipment
- Industrial automation systems
- Key characteristics:
- 4–20+ copper layers
- High gold-plated connector density
- Complex resin structures
Recycling insight:
These boards are the crown jewels of PCB recycling. Advanced sorting systems use AI vision, density separation, and magnetic sorting to isolate them for premium downstream recovery.
Why it matters: High-grade PCBs can yield 5–10 times more precious metals than low-grade boards.
4. Computer & Server Motherboards
Common sources:
- Desktop PCs
- Data centers
- Laptops
- Key characteristics:
- Dense IC chips
- Gold fingers
- Multilayer construction
Recycling insight:
Most PCB recycling lines treat motherboards as a separate category due to their exceptional metal value. Pre-sorting ensures they are processed under optimal conditions to avoid metal loss.
Pro tip: Dedicated motherboard streams significantly improve ROI.
5. Mobile Phone & Consumer Electronics PCBs
Common sources:
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Wearables
- Key characteristics:
- Small size
- Extremely high precious metal concentration
- Miniaturized components
Recycling insight:
Despite their size, these PCBs are precious-metal-rich. Advanced PCB sorting lines use fine-grading and precision shredding to handle them without excessive dust or loss.
Did you know? One ton of smartphone PCBs can contain more gold than one ton of mined ore.
6. Automotive & EV Circuit Boards
Common sources:
- Electric vehicles
- Battery management systems
- ADAS and control units
- Key characteristics:
- Thick copper layers
- Heat-resistant substrates
- Mixed aluminum and copper
Recycling insight:
Modern PCB recycling lines are increasingly designed to process automotive-grade boards, which are heavier, tougher, and more complex than consumer electronics PCBs.
Future-proofing tip: EV-related PCBs are one of the fastest-growing recycling streams globally.
7. Industrial & Telecom Circuit Boards
Common sources:
- Base stations
- PLC systems
- Medical and aerospace electronics
Key characteristics:
- Long service life
- High reliability components
- Often conformal-coated
Recycling insight:
PCB sorting systems remove coated and specialty boards into dedicated streams, ensuring coatings don’t interfere with metal separation efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can one PCB recycling line handle all PCB types?
Yes—with modular configuration. Modern lines use adjustable sorting, shredding, and separation modules to adapt to different PCB grades.
Do PCBs need to be manually sorted first?
Minimal manual sorting is needed. Automated optical and density-based sorting now handles most classification tasks.
What PCBs are most profitable to recycle?
High-grade PCBs, motherboards, and mobile phone boards offer the highest metal yield per ton.
A modern PCB sorting and recycling line isn’t just a machine—it’s a strategic advantage.
From low-grade appliance boards to high-value server and EV PCBs, today’s advanced systems can process an impressive range of circuit boards with speed, precision, and profitability.
As e-waste volumes surge and metal prices rise, knowing exactly what types of PCBs your line can handle is no longer optional—it’s essential.
